【Research Keywords】
Endothelial cell, Vascular function, Rho-associated kinase, Angiogenesis, Regenerative medicine for radiation injury
【Recent highlights】
Application and challenges for future as following: explanation of further the mechanism of production of new blood vessels after cell therapy; establishment of bone marrow bank center; effective and safer method to culture autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell or adipocyte derived stroma cell. It is thought that the technology also improves severe vascular endothelium damage, including vascular injury induced by radiation. An automated culture facility is under development for practical application in near future.
We reported that the role of endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis. In addition, we have shown the differentiation system of endothelial cells. We would like to clarify the mechanisms of development, differentiation, and induction of endothelial progenitor cells. It is expected that evaluation of the role of endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis leads to the development of new strategy for anti-atherosclerosis. ROCK is associated with the onset and progression of atherosclerosis, leading to cardiovascular diseases. ROCK has two isoforms, viz. ROCK1 and ROCK2. We are trying to reveal the downstream signaling pathways on ROCK1 and/or ROCK2 using not only ROCK1/2 knockout mice but also cells isolated from the mice. In addition, we are also focusing on the possibility of ROCK activity as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease.

【Department of Regenerative Medicine】
| Name | Title |
| HIGASHI Yukihito | Professor |
| MARUHASHI Tatsuya | Associate Professor |
| KISHIMOTO Shinji | Assistant Professor |
| Farina Binti Mohamad Yusoff | Assistant Professor (Special Appointment) |
【Major Papers of the Laboratory】
・Association of cumulative low-density lipoprotein cholesterol exposure with vascular function, J Clin Lipidol ., 202403
・Sparing and enhancing dose protraction effects for radiation damage to the aorta of wild-type mice, Int J Radiat Biol, 202308
・Effect of ipragliflozin on carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial, Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, 202302
【Education・Research】
Large amount of bone marrow is required to be harvested, and therapy is limited to one transplantation because of technical issues and stress, while repeated treatments are effective in some cases. In our new technology, we culture and grow harvested autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell and adipocytes derived stroma cell from small amount of sample, to make repeated treatment possible. Application and challenges for future as following: Explain further the mechanism of production of new blood vessels after cell therapy. Establish bone marrow bank center to culture bone marrow cells for repeated transplantation to improve effectiveness of therapy. Application to regenerative treatment to skin, liver cells, and the heart. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell implantation is established to be effective as treatment for those patients with severe artery occlusion, avoiding limb amputation. It is thought that the technology also improves severe vascular endothelium damage, including vascular injury induced by radiation. In addition, effective and safer method to culture autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell or adipocyte derived stroma cell is established for repeated treatments and reduced stress for patients. An automated culture facility is under development for practical application in near future. Endothelial dysfunction is the initial step of atherosclerosis. We reported that the role of endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis. In addition, we have shown the differentiation system of endothelial cells. We would like to clarify the mechanisms of development, differentiation, and induction of endothelial progenitor cells. It is expected that evaluation of the role of endothelial cells and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis leads to the development of new strategy for anti-atherosclerosis. We are evaluating the possibility of new concept of angiogenesis other than exisiting cell therapy and gene therapy. Recently, we have shown with collaborators that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound induces angiogenesis in a mice model of ischemic limb through the activation of PGC-1α/angiopoetin-1/ERK/VEGF pathway. In addition, we acquired a patent regarding system of angiogenesis induced by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and developed new modality using low-intensity pulsed ultrasound system. A clinical trial using a new modality is preparing for undergoing in patients with critical limb ischemia. Recently, there is accumulating evidence that the increase on Rho-associated coiled-coil forming kinase (ROCK) activity could evoke the onset and progression of cardiovascular disease. Activated RhoA binds to ROCK, leading to the regulation of downstream targets of ROCK, resulting in progression of atherosclerosis and subsequent cardiovascular disease. So far, we have demonstrated in clinical studies that ROCK activity is increased in smokers, a human model of oxidative stress, ROCK activity substantially correlates with endothelial dysfunction, and aging-related increase on aortic stiffness is mediated through vascular ROCK activity. We have further revealed several mechanisms of ROCK-mediated atherosclerosis by in vitro and in vivo studies. It is known that ROCK has two isoforms, viz. ROCK1 and ROCK2. Also, recent studies have shown the functional difference between the two isoforms. Therefore, we are now focusing on the downstream signaling pathway on ROCK1 and/or ROCK2 using not only ROCK1/2 knockout mice but also cells isolated from the mice. In addition, we are working on translational study, viz. bench to bedside, by evaluating the clinical usefulness of vascular ROCK activity by Starin-gauge plethysmography and leukocyte ROCK activity by Western blot analysis in patients with cardiovascular disease.
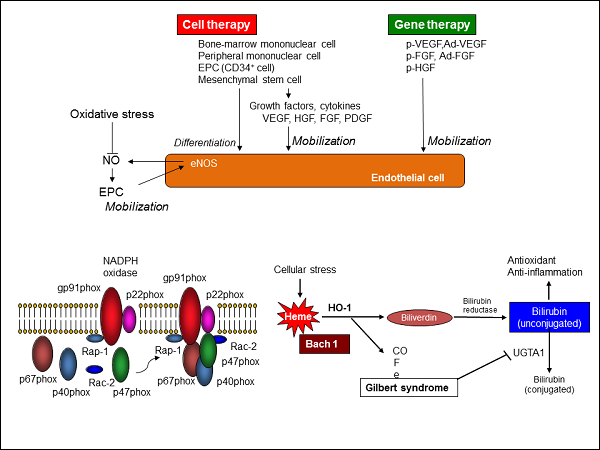
【Figure explanation】 Development of cell therapy, cell repair, and angiogenic biology for regenerative medicine/Repair system of genome damage induced by radiation in endothelial cells/Role of endothelial cells/endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis
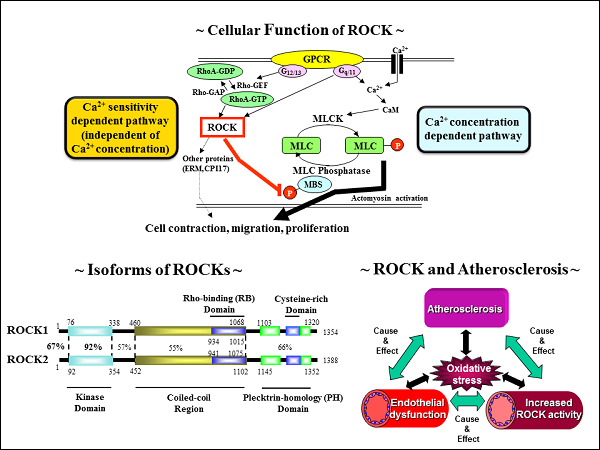
【Figure explanation】 Role of ROCK as a mediator and a biomarker for cardiovascular disease

 Home
Home

