Professor Naoki ISOBE
School of Applied Biological Science, Hiroshima University
Tel:082-424-7993 FAX:082-424-7993
E-mail:niso*hiroshima-u.ac.jp (Note: Please replace *with @)
Key points of this research
- In the mammary gland of cows, inflammation (mastitis) caused frequently by bacterial infection reduces milk quality and quantity.
- Bacterial infection can be prevented by understanding immune function.
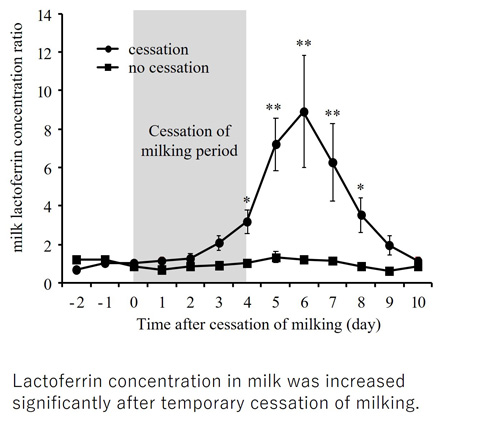
- Protein-level elucidation of the mastitis treatment method (temporary cessation of milking) is proposed.
Content of research
Bacteria often invade into the mammary gland but are usually eliminated by the immunity of the mammary gland. However, if the cow is unhealthy or stressed, this may reduce immunity and may not kill bacteria. Then, bacteria proliferate in the mammary gland which becomes infected, resulting in inflammation. This condition is called mastitis. Mastitis causes decreased quality and milk yield, so it causes huge economic losses for farmers. Therefore, it is necessary to maximize cow immunity to bacteria. With immunity, antimicrobial components can be activated as soon as bacteria invade and eliminate a broad spectrum of bacteria unlike antibodies. In this paper, we examined how antibacterial components are involved in the method of temporary cessation of milking, which was recently developed in Japan as a treatment for mastitis.
Goats were used as a model animal instead of cows. Milking was stopped for 3 days followed by normal milking. It was found that the concentration of antimicrobial components (defensin, S100A7, lactoferrin, etc.) increased dramatically after milking cessation. These results indicated that antimicrobial components contribute greatly to the elimination of infectious bacteria by the temporary cessation of milking.
In the future, we aim to link these antimicrobial components to prevention and treatment methods by examining suitable conditions to further increase these antibacterial components. We also believe that if we can produce milk with a lot of antibacterial components, we can maintain human health by drinking it or using it as a treatment for infectious diseases.
Information details of publication
- Journal: JOURNAL OF DAIRY SCIENCE
- Title: Effect of temporary cessation of milking on the innate immune components in goat milk
- Authors: Fika Yuliza Purba, Yoshihisa Ishimoto, Takahiro Nii, Yukinori Yoshimura, Naoki Isobe
- DOI: 10.3168/jds.2021-20564


 Home
Home

