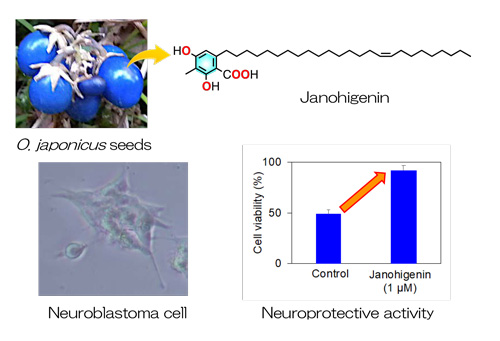
The perennial herbaceous plant Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb.) Ker Gawl. (Asparagaceae, Japanese name: janohige) is widely distributed in East Asia, used as a weed-suppressing cover crop and as a medicinal plant for ameliorating physiological thirst and treating sore throats, acute chronic inflammation, bacterial infections, and cardiovascular diseases.
In the course of our investigations into biologically active compounds, we isolated eight hitherto undescribed long-chain anacardic acid derivatives, designated as janohigenins, from O. japonicus seeds. Janohigenins exhibited noticeable neuroprotective activity against rotenone-induced cellular damage in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells at 1 µM. The findings of this study revealed that janohigenins could provide promising therapeutic candidates for treating neurodegenerative disorders.


 Home
Home