Assistant Professor Yusaku TSUGAMI
School of Applied Biological Science, Hiroshima University
Tel:082-424-7993
E-mail:ytsugami*hiroshima-u.ac.jp (Note: Please replace *with @)
Key points of this research
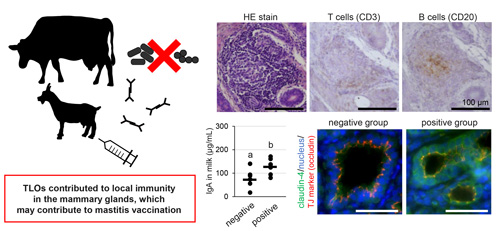
- Out of 30 udders of lactating goats, 19 showed tertiary lymphoid organs.
- IgG and IgA concentrations in milk were significantly higher.
- Localization and amount of claudin-4 changed, indicating leakage at tight junctions.
Content of research
Ectopic tertiary lymphoid organs (TLOs) have been identified in many organs, such as the lungs, nasal cavities, and kidneys of both mice and humans. Although lymphocyte aggregates have been observed in the mammary glands of ruminants, the details remain unclear. In this study, we investigated the mammary glands of lactating goats for the presence of TLOs. The localization of CD20 (B cells), CD3 (T cells), MECA79 (high endothelial venules), CD40 (follicular dendritic cells), and IgA was examined by immunohistochemistry. The concentrations of IgG and IgA in milk were measured by ELISA. The localization and amount of tight junction (TJ) proteins (claudin-3 and claudin-4) were examined using immunofluorescence and western blotting. We found that 19 out of 30 udders contained lymphocyte aggregates, which showed positive reactions against CD20, CD3, CD40, and MECA79. These results indicate that mammary glands of lactating goats contain TLOs. The IgG and IgA concentrations in the milk of TLO-positive goats and the number of IgA-positive cells were higher than those in negative goats. Furthermore, claudin-4 was localized in the TJ region and the amount was higher in TLO-positive mammary glands than that in the negative group, indicating the presence of leakages at TJs. In conclusion, a majority of lactating goat udders have TLOs, which contribute to local immunity by producing immunoglobulins.
Information details of publication
- Journal: Frontiers in Immunology
- Title: Investigating mammary glands of lactating goats for the presence of tertiary lymphoid organs
- Authors: Tsugami Y, Nakayama S, Suzuki N, Nii T, Isobe N
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.941333


 Home
Home

