Key points of this research results
- The hydrogen desorption kinetics of MgH2 was improved by addition of Cu-PANI composite.
- The hydrogen desorption reaction proceeded at about 300℃, which was lower than that of MgH2 itself.
- The optimum conditions of sample synthesis were investigated to obtain the higher catalytic activity of Cu-PANI.
Outline
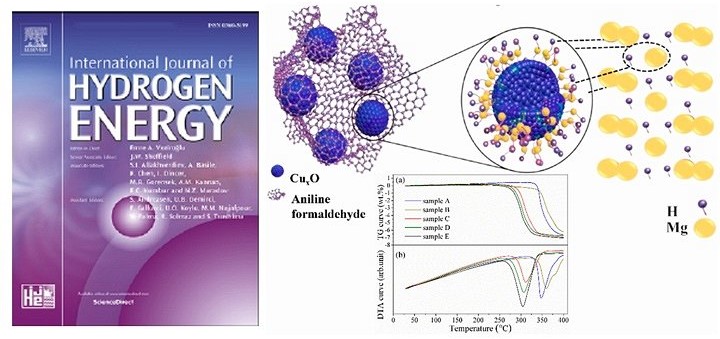
Magnesium hydride (MgH2) is attractive medium to compactly store 「Hydrogen (H2)」, which is expected as an energy medium at next generation, because of high gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen density. On the other hand, since the hydrogen desorption and absorption reactions are sluggish, an improvement of kinetics by catalysts and scaffolds is main research issue of the Mg-H2 system.
In this work, additive effects of copper (Cu) - aniline formaldehyde Co-polymer (PANI) composite for MgH2 were investigated to improve the reaction kinetics as international collaboration work with Prof. Ankur Jain group of Suresh Gyan Vihar University in India. By dispersing 10 wt.% of Cu-PANI composite on the MgH2 surface under suitable conditions, the hydrogen desorption temperature was successfully decreased compared with that of MgH2 without catalysts, in which activation energy of the reaction is lowered by the catalytic effects of Cu-PANI composite. Although further research is required to understand the catalytic mechanisms of Cu-PANI composite, the results obtained in this work are expected as guideline to design catalysts for the Mg-H2 system.
The results of this work was highly evaluated in a field of hydrogen storage materials and published as article in scientific journal 「International Journal of Hydrogen Energy」 (Q1 journal).
Paper Info
P. Khandelwal, Z. Chen, C. Prakash, K. Shrivastava, F. Guo, H. Miyaoka, T. Ichikawa, A. Dixit and A. Jain
Copper oxide – PANI derived novel composites for the kinetic tuning of MgH2
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy (2024) (IF: 8.1, Q1 journal)
doi:10.1016/J.IJHYDENE.2024.02.379.

 Home
Home



