Introduction of department
In Department of Pediatric Dentistry Hiroshima University Hospital, we pay attention to not only oral status such as dental caries in deciduous or immature tooth and malocclusion, but also psychological status and living environment of the patients. After treatment of acute diseases, patients should be placed under periodical dental check-up to maintain their oral health. Our specialists provide comprehensive oral care focused on the individual needs of children.
Treatment and prevention of dental caries, occlusal guidance and treatment of tooth injury in deciduous and immature teeth are mainly performed for children. Moreover, treatments of impacted tooth, and periodontal disease in primary or mixed dentition are especially performed.
Our patients are included all the children with general, non-cooperation, intellectual disability and systematic disease. We have solutions for oral health of children.

clinical conference is open on every Friday
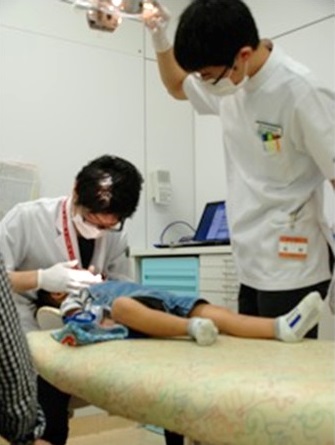
Ordinary treatment at Pediatric dental clinic

The pediatric dental clinic is placed at same area with Pediatrics and Pediatric surgery
Research content
- Bacteriological study on dental caries pathogenesis and prevention in children
- Molecular biological research of oral bacteria in children
- Clinical study of oral care of children with systemic diseases
- Evaluation of the stress of dental treatment against children
- Three-dimensional analysis on the growth of the dentition in children
- Clinical approach to dysphagia in children
- Research on the relationship between periodontal disease and systemic conditions in child or pregnant woman
Treatment achievements
Number of cases (per year)
- Occlusal guidance (treatment and prevention of malocclusion until mixed dentition) (200 cases)
- Dental treatment for disabed children (200 cases)
- Dental treatment for children with systemic diseases (150 cases)
- Replantation of dislocated teeth (60 cases)
- Extraction of impacted supernumerary teeth including mesiodens (35 cases)
- Fenestration and occlusal guidance of impacted teeth (20 cases)

 Home
Home