E-mail: ino*hiroshima-u.ac.jp (Please replace * with @)
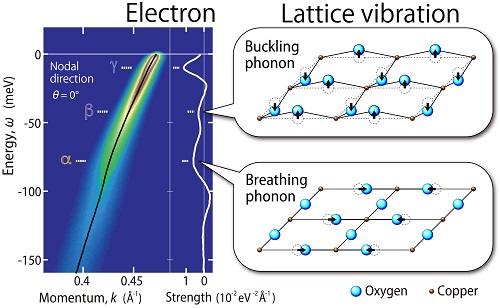
Conventional superconductivity is caused by electron-phonon coupling. The discovery of high-temperature superconductors raised the question of whether such strong electron-phonon coupling is realized in cuprates. Strong coupling with some collective excitation mode has been indicated by a dispersion “kink.” However, there is intensive debate regarding whether the relevant coupling mode is a magnetic resonance mode or an oxygen buckling phonon mode. This ambiguity is a consequence of the energy of the main prominent kink. The research group of Associate Professor Akihiro Ino shows a new landscape of dispersion kinks. They report that heavily overdoping a Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 superconductor results in a decline of the conventional main kink and a rise of another sharp kink, along with substantial energy shifts of both. Notably, the latter kink can be ascribed only to an oxygen-breathing phonon. Hence, the multiple phonon branches provide a consistent account of our data set on the multiple kinks. Their results suggest that strong electron-phonon coupling and its dramatic change should be incorporated into or reconciled with scenarios for the evolution of high-Tc superconductivity.
Full bibliographic information
- Title: A New Landscape of Multiple Dispersion Kinks in a High-Tc Cuprate Superconductor
- Authors: H. Anzai, M. Arita, H. Namatame, M. Taniguchi, M. Ishikado, K. Fujita, S. Ishida, S. Uchida, and A. Ino
- Journal: Scientific Reports 7, Article number: 4830 (2017)
- doi:10.1038/s41598-017-04983-0
- Profile of Associate Professor (Special Appointment) Akihiro Ino
- Official Website of the Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center (HiSOR)
*The Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center (HiSOR) calls for collaborative research proposals using synchrotron radiation in the vacuum ultraviolet and soft x-ray regions. Please visit the webpage for details.
Akihiro Ino, Associate Professor (Special Appointment)
Hiroshima Synchrotron Radiation Center


 Home
Home

