Email: pr-research*office.hiroshima-u.ac.jp (Please change * into @)
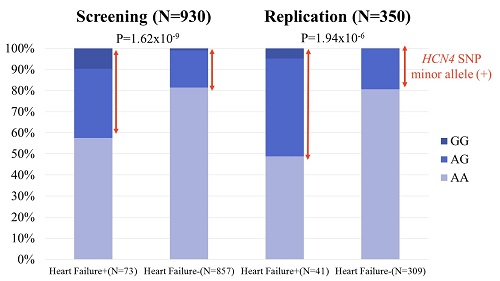
The HCN4 SNP rs7164883 independently increases risk of heart failure in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Scientists in Japan have found a potential marker to identify which people with abnormally fast heartbeats are at high risk of developing heart failure.
The results were published in June in Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine, a journal from the American Heart Association.
Atrial fibrillation, or chronically, abnormally fast heartbeat, can be a symptom of a potentially fatal disease known as tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy (TIC). The condition can be reversed and damage can be prevented, but only if the heartbeat is brought back into proper rhythm through drugs or catheter therapy. TIC is currently only diagnosed after ruling out other potential heart disorders, and little is known about risk factors for TIC, according to study author Yukiko Nakano, an associate professor at the Graduate School of Biomedical & Health Sciences at Hiroshima University.
Now her team has taken a step toward diagnosing and treating the condition more quickly. The researchers identified a genetic marker that indicates when a person with a fast heartbeat is more likely to develop TIC and, eventually, heart failure. Heart disease is the third cause of death in Japan, according to the World Health Organization,
“Atrial fibrillation is the most common cause of TIC in patients without a history of structural heart diseases,” Nakano wrote. “Poorly controlled ventricular rates may worsen ventricular function, but only a fraction of patients with atrial fibrillation develop TIC.”
Previous studies have identified 26 genetic variants associated with atrial fibrillation. Of these, only two are cardiac ion channel genes, which help regulate the heart’s conduction. The gene HCN4 is the only one that is known to have a critical function in the autonomic control of heart rate, so Nakano and her team investigated how small changes in the gene could indicate a greater risk for developing heart failure in a study of 73 patients. The genetically different HCN4 marks which patients are at increased risk for heart failure.
While the researchers plan to further validate their results with a larger study cohort, they’re hopeful that they’re on the right track to help people at risk for cardiac damage or even death.
“We will be able to distinguish the high-risk atrial fibrillation patients developing heart failure and consider [them] for early therapeutic intervention,” Nakano said. “We can prevent their heart failure by stricter heart rate control or early rhythm control [using currently available heart devices and drugs].”
Nakano also said that this genetic marker could potentially serve as a therapeutic target for the development of a drug to help patients with atrial fibrillation maintain or restore a healthy heart rhythm.
This research was supported in part by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. Other contributors include clinicians and researchers from the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine and the Department of Gastroenterology and Metabolism at the Hiroshima University Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, the Laboratory for Digestive Diseases at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences, the Liver Research Project Center at Hiroshima University, the Department of Internal Medicine at Chuden Hospital, the Department of Molecular Physiology at the Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and the Department of Cardiology at the Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daini Hospital.
Full bibliographic information
- Title: HCN4 Gene polymorphisms are Associated with Occurrence of Tachycardia Induced Cardiomyopathy in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Authors: Yukiko Nakano*, Hidenori Ochi, Akinori Sairaku, Yuko Onohara , Takehito Tokuyama, Chikaaki Motoda, Hiroya Matsumura, Shunsuke Tomomori, Michitaka Amioka, Naoya Hironobe, MD, Yousaku Ohkubo, Shou Okamura, Naomasa Makita, Yukihiko Yoshida, Kazuaki Chayama, and Yasuki Kihara
*Corresponding author - Journal: Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine
- doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.117.001980
- Profile of Associate Professor Yukiko Nakano
- Find more Hiroshima University research news on our Facebook page
Norifumi Miyokawa
Research Planning Office, Hiroshima University

 Home
Home