E-mail: nohe*hiroshima-u.ac.jp (Please replace * with @)
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is an important medical remedy for acute radiation syndrome as well as widely accepted treatment for intractable hematologic diseases. However, development of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a serious complication after HCT and frequently associated with high morbidity. To develop a novel preventive/therapeutic strategy for post-transplant GVHD, the Department of Hematology and Oncology at the Research Institute for Radiation Biology and Medicine recently discovered that nanosized extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (BM-MSCs) have unique functions to ameliorate GVHD-associated organ damages in a collaborative research with Kyoto University. Systemic infusion of EVs suppressed the functional differentiation of naïve T cells to an effector phenotype and prolonged the survival of mice with GVHD. These results pave the way for the novel therapy for HCT-associated GVHD and systemic T-cell activated diseases by use of BM-MSC-derived EVs. (A part of this work was presented at the 2017 Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology.)
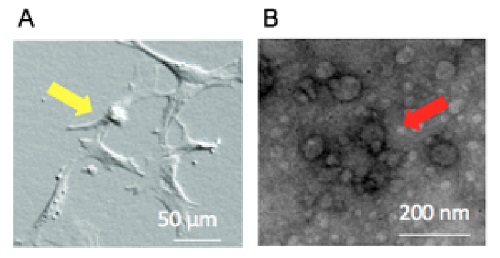
A) Bone marrow-derived MSCs and B) nanosized MSC-derived extracellular vesicles
Reference
Fujii S, et al. Stem Cells. 2017 Dec 14 [EPub ahead of print]
doi: 10.1002/stem.2759.
Professor Tatsuo Ichinohe
Research Institute for Radiation Biology and Medicine, Hiroshima University

 Home
Home